Eustachian Tube Obstruction (infant/toddler)
Stuttering
June 21, 2017
Warning Signs of a Toddler’s Language Delay
June 28, 2017The Eustachian tube is behind the eardrum. It connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The tube is usually closed. But it opens during yawning or swallowing. This helps make the air pressure in the middle ear the same as outside the ear. The tube also drains mucus made in the middle ear. A blocked tube is called a Eustachian tube obstruction. It is most common in babies whose tubes are small and still forming.
A Eustachian tube that is blocked causes pressure, pain, and loss of hearing. Sounds may be muffled. The ear may feel full. A child who is too young to talk may cry and pull at the ear. An older child may complain of pain or trouble hearing. An obstruction can sometimes lead to an ear infection.
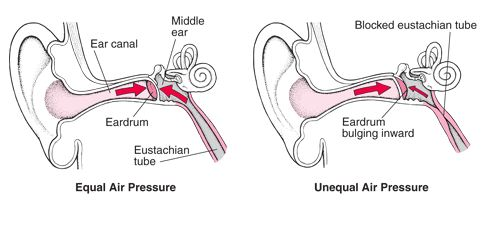
The blockage often goes away on its own without treatment. Nasal decongestants, nasal sprays, or allergy treatments may help ease swelling within the tube. Obstructed Eustachian tubes are usually a short-term problem.
Home care
Follow these guidelines when caring for your child at home:
- Your child’s health care provider may prescribe medicines to reduce fluid and inflammation, or to treat an ear infection. Follow the doctor’s instructions for giving these medicines to your child.
- Keep your baby’s head upright when giving a bottle to prevent formula from going into the Eustachian tube.
- Keep your child’s ear canal dry. Have your child wear ear plugs when taking a bath or playing in a pool.
- Teach your older child to swallow or yawn to open the tubes and equalize pressure.
- Flying in an airplane causes pressure to build up in the Eustachian tube, especially during take-off and landing. This can be especially painful for young children. Breastfeed or bottle-feed your baby during take-off and landing to help prevent ear pain. Have older children swallow or yawn.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your child’s health care provider, or as advised.
- When to seek medical advice
- Call your child’s health care provider right away if:
- Your child is 3 months old or younger and has a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher. Your child may need to see a health care provider.
- Your child is of any age and has fevers higher than 104°F (40°C) that come back again and again
- Also call your child’s provider right away if any of these occur:
- Hearing loss or trouble hearing
- Symptoms last longer than a few weeks
- Redness or swelling in the ear gets worse
- Pain gets worse
- Foul-smelling fluid drains from the ear.
References: Online
- https://www.fairview.org/HealthLibrary/Article/512080EN
- https://www.google.co.in/search?q=Eustachian+Tube+Obstruction&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiYxdaQnP7SAhULV7wKHWXRAFEQ_AUIBigB&biw=1366&bih=638#imgrc=opiZl6RLv_UhsM:



